Differential Evolution (SciPy)
Differential evolution (DE), proposed by Storn and Price [1], is a population-based metaheuristic search algorithm that optimizes a problem by iteratively improving a candidate solution based on an evolutionary process.
Usage
To use scipy’s implementation of a Differential Evolution algorithm, import the corresponding functionality from the ACT:
import ACT.scipy as ACTscipy
To start the optimization, call the optimize function:
ACTscipy.optimize(maxiter=500, n_cpu=32, popsize=20, method='DifferentialEvolution')
Example
Exemplarily, the results of a calibration of a hypoplastic model ($\phi_c$, $h_s$, $n$, $e_{c0}$, $e_{d0}$, $e_{i0}$, $\alpha$, $\beta$) for Karlsruhe Fine Sand (BMU-Sand) are shown by means of drained monotonic triaxial tests:
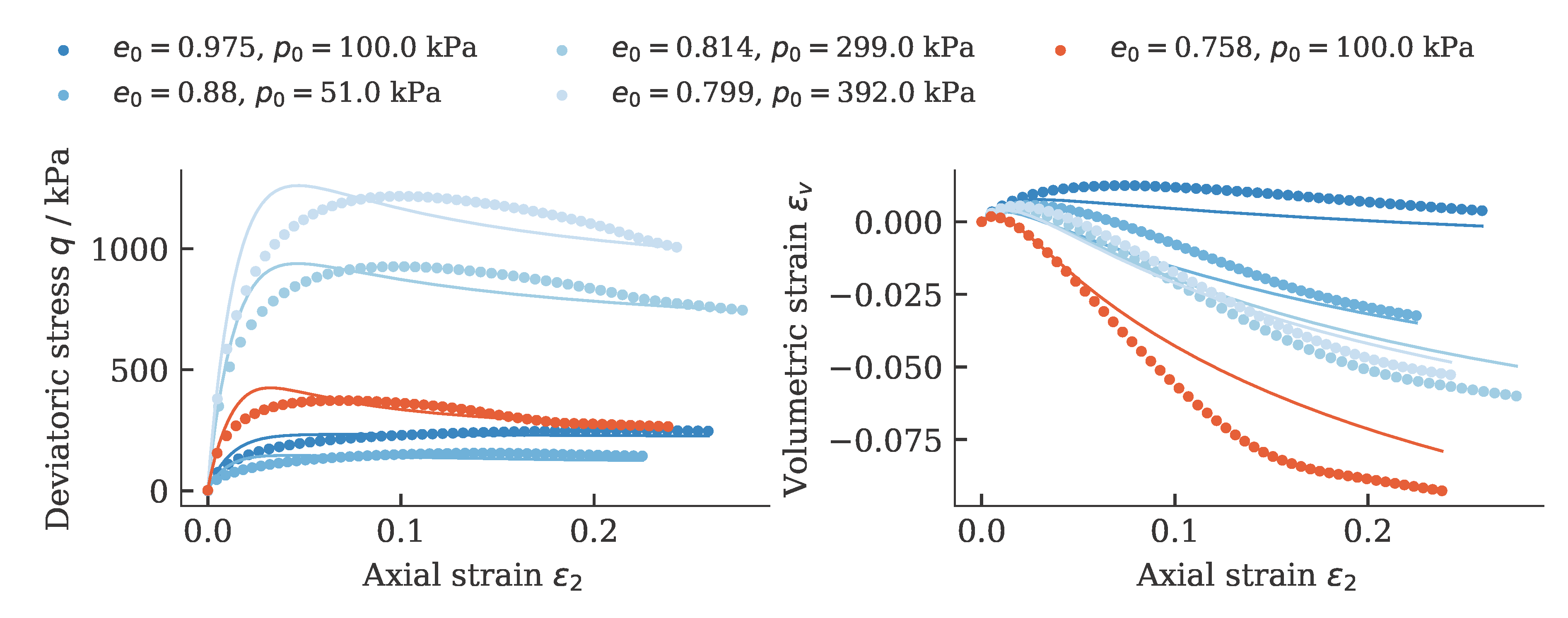
and oedometric compression tests:
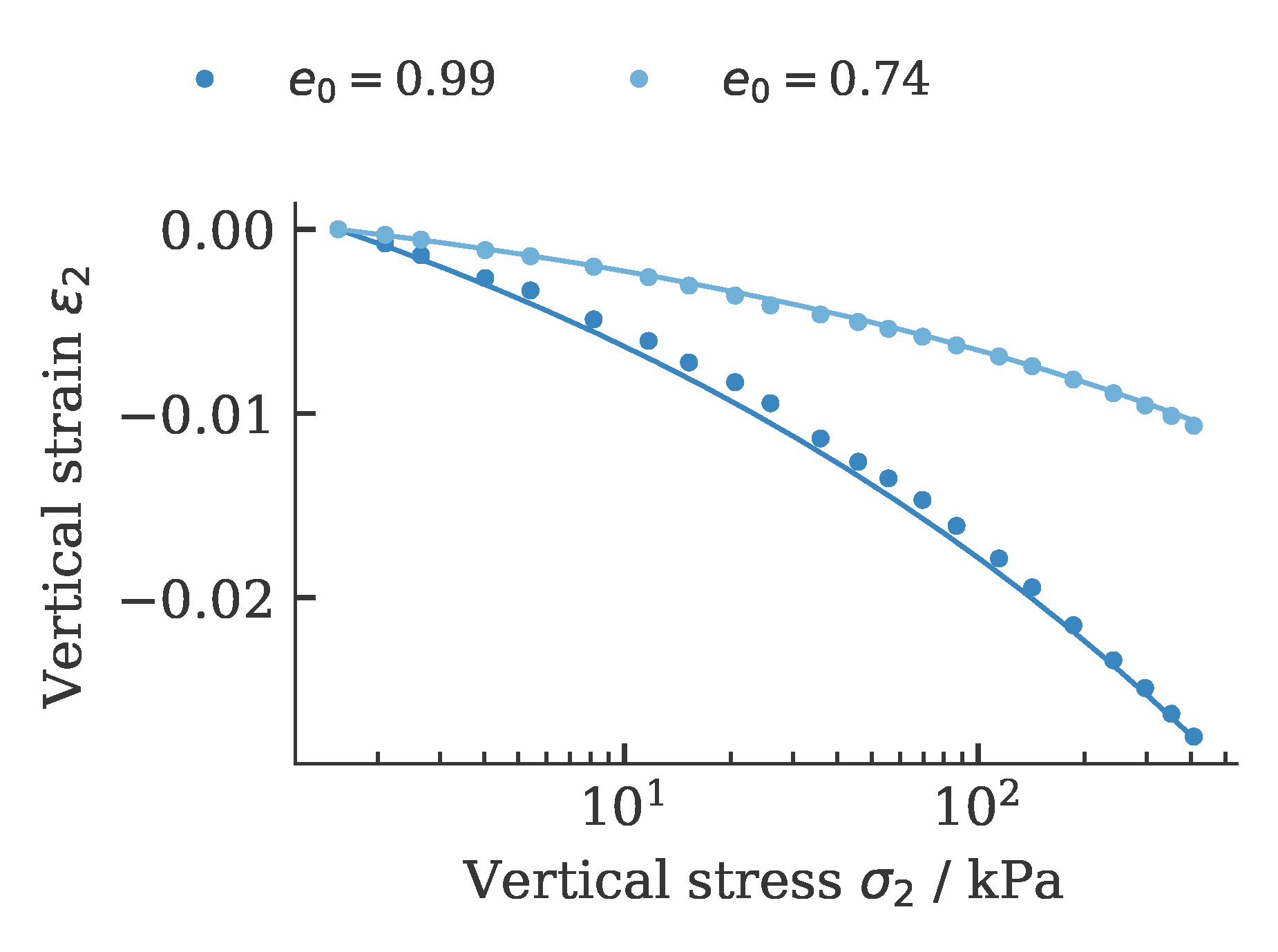
To get an (incomplete) impression about the reproducibility of the results, we repeat the calibration five times. The achieved values of the cost function as well as the required computing time per run (2x AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 3955WX 16-Cores, 3900 MHz, WSL2) are shown below.
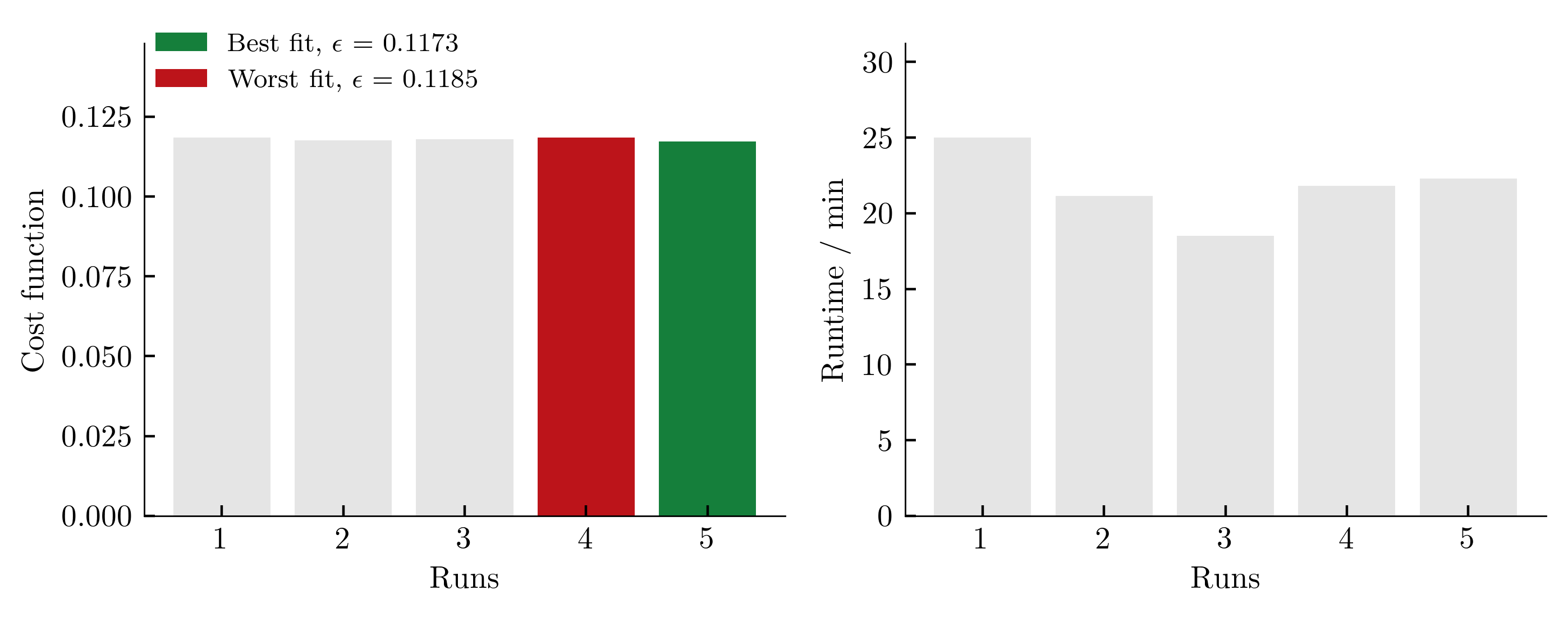
The influence of the scatter in the costfunction on the simulation outcome is shown below (from large variations in cost functions, large variations in simulation results are expected):
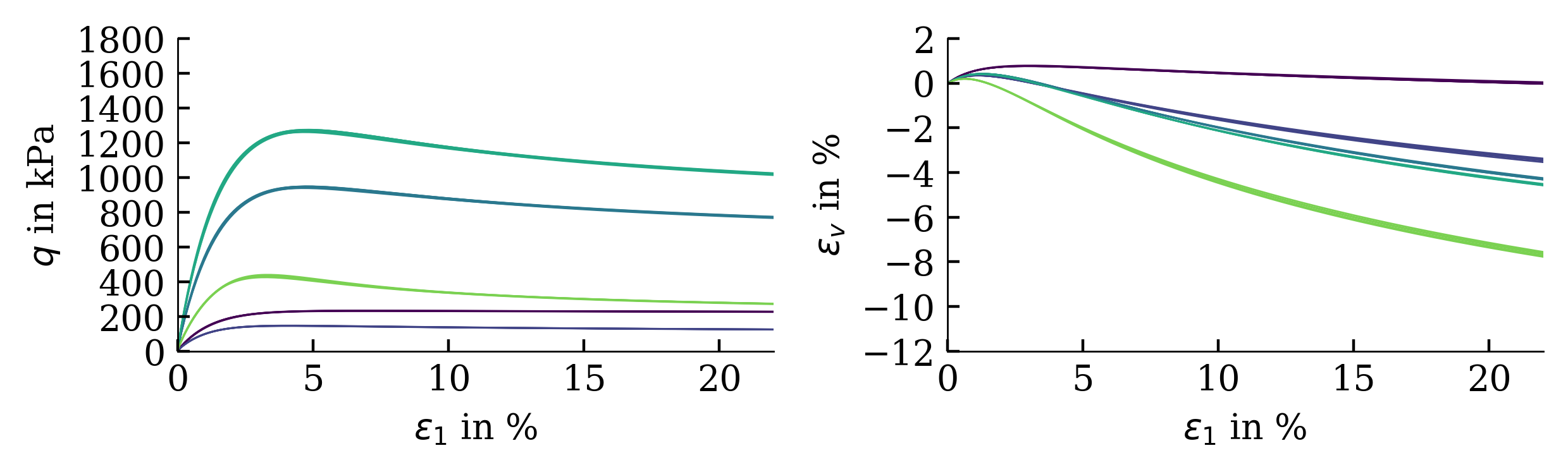
References
[1] Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution - a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Global Optim 11(4):341–359. [[https://doi.org/10.1023/A: 1008202821328]]