Output definition
*Output, <type>, <format 1>, <format 2> [, flush]
*Frequency = <output interval>
*Node, nset = <set name>
<variable 1>, ..., <variable n>
*Element, Elset = < set name>
<variable 1>, ..., <variable n>
*Integration point, Elset = <set name>
<variable 1>, ..., <variable n>
This option defines the output for the current step. <type> can be field, where the specified variables are written to the output file for the visualization, print, where the variables are written to a text file or user, where the specified variables are written to (initial) user files explained here
Output quantities can be requested for different locations in the model:
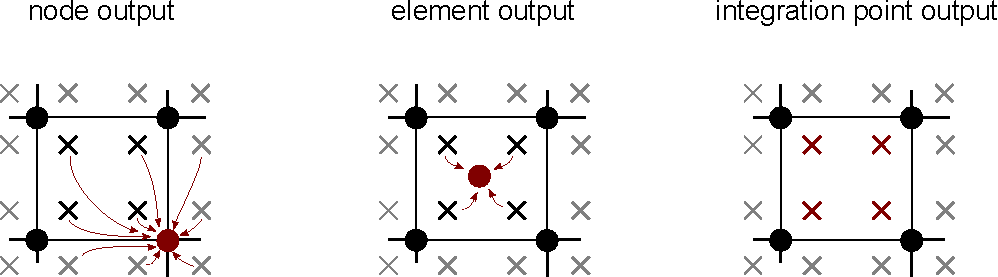
Figure 1. Graphical representation of the location and calculation of the different output variants
-
Node: Output variables which are to be output at the position of the nodes. This option is basically available for all variables that are stored and calculated at the nodes. This includes, for example, displacement (as well as velocity and acceleration), pore water pressure, but also contact variables. For these quantities the output is exact. For output variables which are calculated at the integration points (i.e. within the elements such as stress, strain and state variables of constitutive models), (a) the variables are extrapolated from the integration points to the nodes using the shape functions of the element and (b) the mean value of all contributions of the integration points of elements adjacent to the nodes is calculated. Thus, the node output of integration point variables corresponds to an averaged extrapolated quantity. -
Element:The element output is available for all integration point variables (such as stress, strain and state variables of constitutive models). The element output corresponds to the mean value of all integration points of the element. Smoothing across the element boundaries does not take place. -
Integration point:This form of output is available for all quantities which are stored/calculated at the integration points (such as stress, strain and state variables of constitutive models). Here, the values for each integration point are separately given in the output. Thus, no weighting or smoothing takes place - the output quantities are therefore exact. The output is currently only available as "print output".