1D site response
The aim of this tutorial is to demonstrate the features of numgeo needed to perform (1D) site response analyses. The soil profile considered for this example is demonstrated in Figure 1. A schematic of the finite element model representation of the soil profile is depicted on the right-hand side of Figure 1.
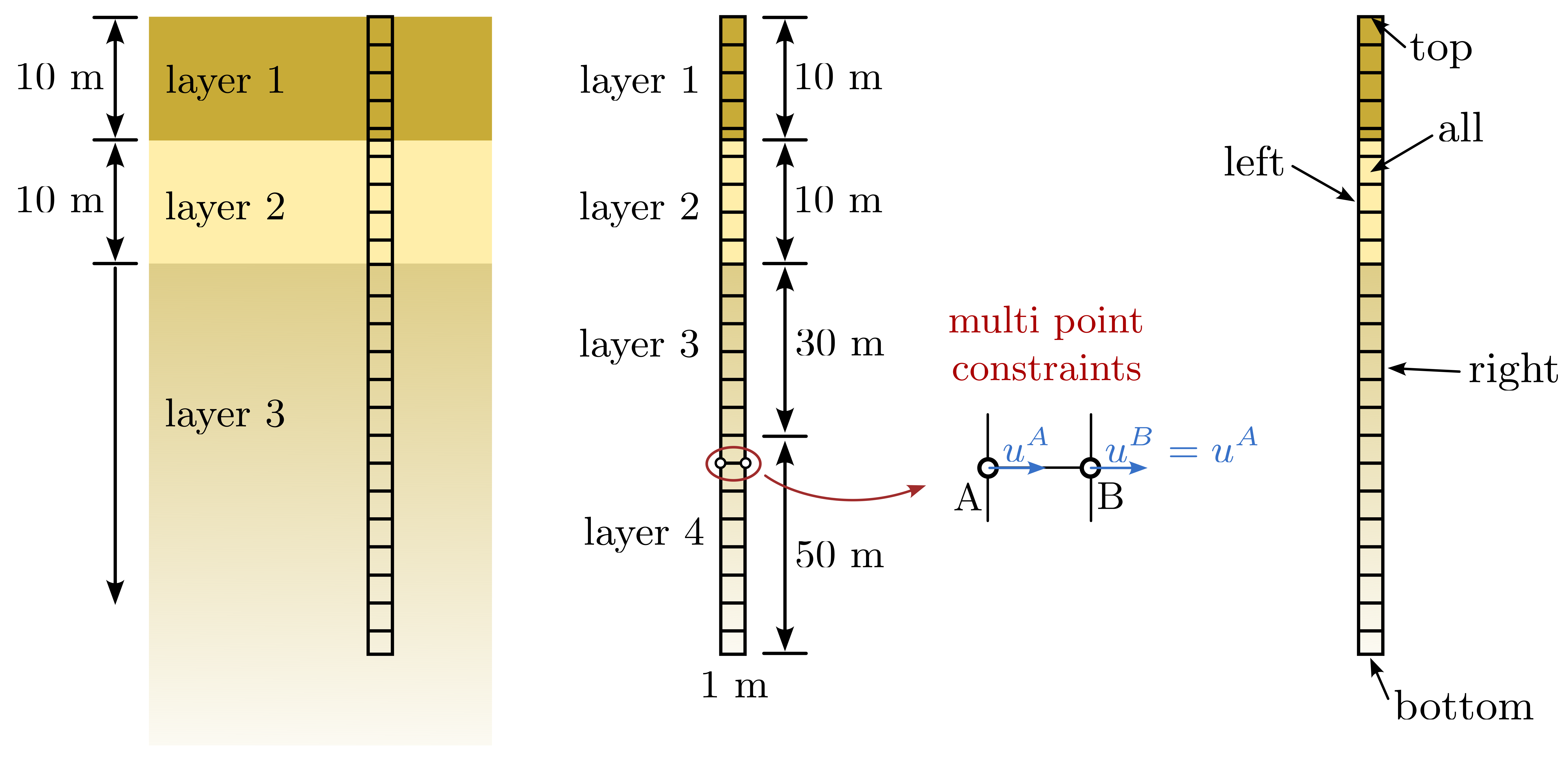
Figure 1. Soil profile used in the conducted site response analyses
A 2D finite element model is created for the simulations. To enforce the 1D conditions, the displacements of the nodes is constrained using multi-point constraints such that the displacements are the same for all nodes at a given elevation.
The finite element model was created using Salome. The corresponding file can be downloaded here.
For easy handling of boundary conditions and loads, the following groups have been defined:
all: element and node set containing all nodes/elements of the modellayer1: element set containing all elements of layer 1layer2: element set containing all elements of layer 2layer3: element set containing all elements of layer 3layer4: element set containing all elements of layer 4bottom: node set containing the nodes of the bottom boundarytop: node set containing the nodes of the top boundaryleft: node set containing the nodes of the left boundaryright: node set containing the nodes of the right boundary
The soil colum is stored as a part named Soil. Access to the sets is thus given by Soil.<set-name>.
Two-phase stabilized reduced integrated elements have been used for the discretization. The nodal unknowns of these elements are the solid displacements \(u_x\) and \(u_y\) as well as the pore water pressure \(p^w\). Linear interpolation is used for both the solid displacements as well as the pore water pressures. Reduced integration is used, i.e. only one integration point located in the center of the element is used for the numerical integration. The finite element mesh can be downloaded here
The following two scenarios are investigated in the following sections: